Grammar of graphics
Jeff Stevens
2023-03-31
Introduction
Set-up
Plotting with {ggplot2}

Grammar of graphics

Seven components/layers of ggplots
- Data
- Mappings – maps data to properties of geom
- Geom – represents data
- Stat – transforms data
- Position – control placement of data on coordinate
- Facet – split graph into subplots
- Coordinate – places data in coordinate system
Seven components/layers of ggplots
Full specification of plot
ggplot(data = penguins) +
geom_point(
mapping = aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm),
stat = "identity",
position = "identity"
) +
coord_cartesian() +
facet_null()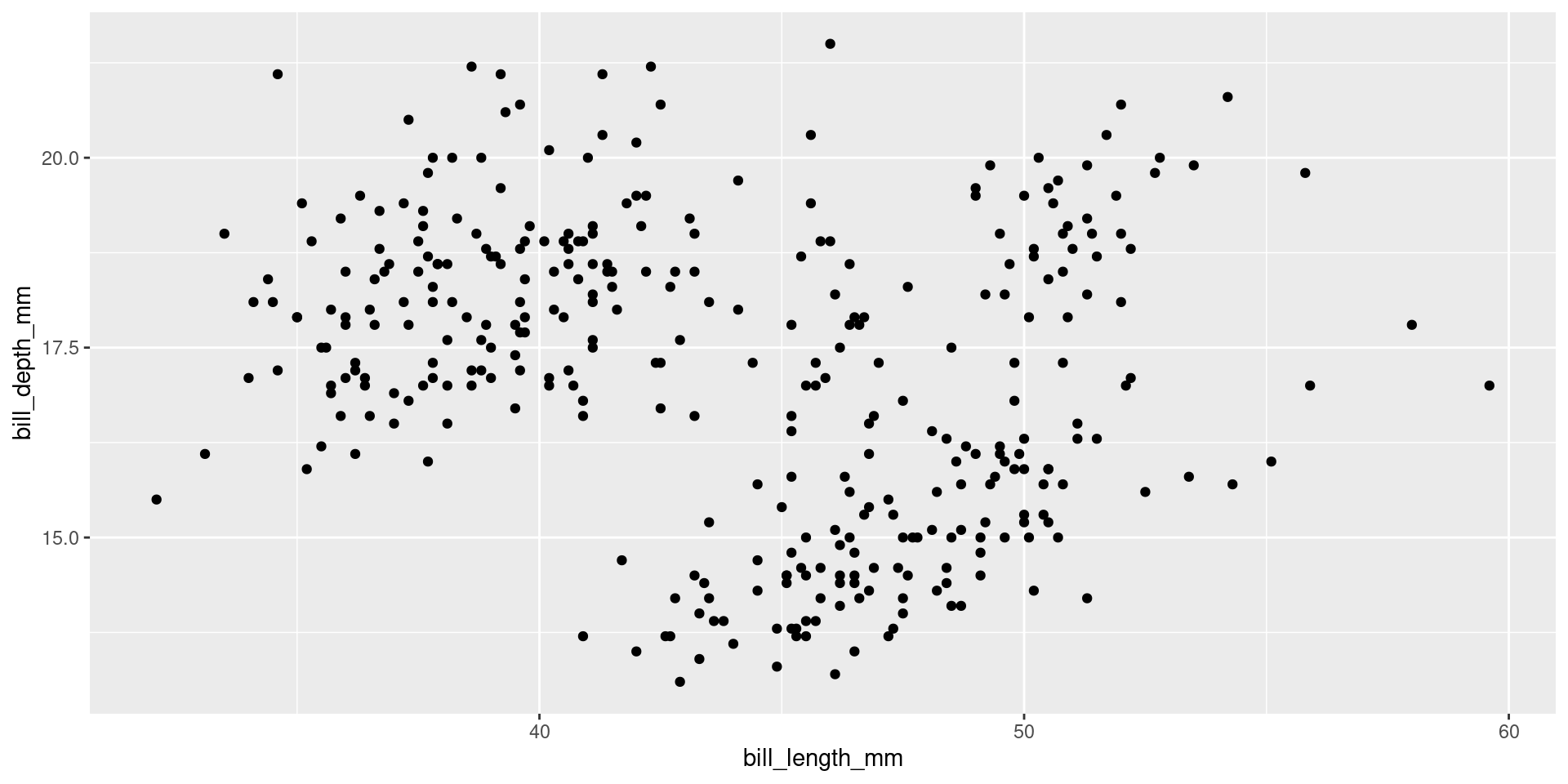
Data
Tidy data
Data should be in tidy format for ggplots
mpg# A tibble: 234 × 11
manufacturer model displ year cyl trans drv cty hwy fl class
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <int> <chr> <chr> <int> <int> <chr> <chr>
1 audi a4 1.8 1999 4 auto… f 18 29 p comp…
2 audi a4 1.8 1999 4 manu… f 21 29 p comp…
3 audi a4 2 2008 4 manu… f 20 31 p comp…
4 audi a4 2 2008 4 auto… f 21 30 p comp…
5 audi a4 2.8 1999 6 auto… f 16 26 p comp…
6 audi a4 2.8 1999 6 manu… f 18 26 p comp…
7 audi a4 3.1 2008 6 auto… f 18 27 p comp…
8 audi a4 quattro 1.8 1999 4 manu… 4 18 26 p comp…
9 audi a4 quattro 1.8 1999 4 auto… 4 16 25 p comp…
10 audi a4 quattro 2 2008 4 manu… 4 20 28 p comp…
# ℹ 224 more rowsData to ggplot
Data inside ggplot()
ggplot(data = mpg)
Data to ggplot
Data piped to ggplot()
mpg |>
ggplot()
Data to ggplot
Process data before plotting
mpg |>
filter(class != "2seater") |>
mutate(class = str_to_sentence(class)) |>
ggplot()
Mapping
Map data to positions
Specify columns for x and y
Map data to positions
Equivalent but not ideal. Why?
Map data to positions
This is how we’ll do it
Geometric objects
Geoms
There are many different ways of representing data on a plot

Plot points
Add geom_point()
mpg |>
ggplot(aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point()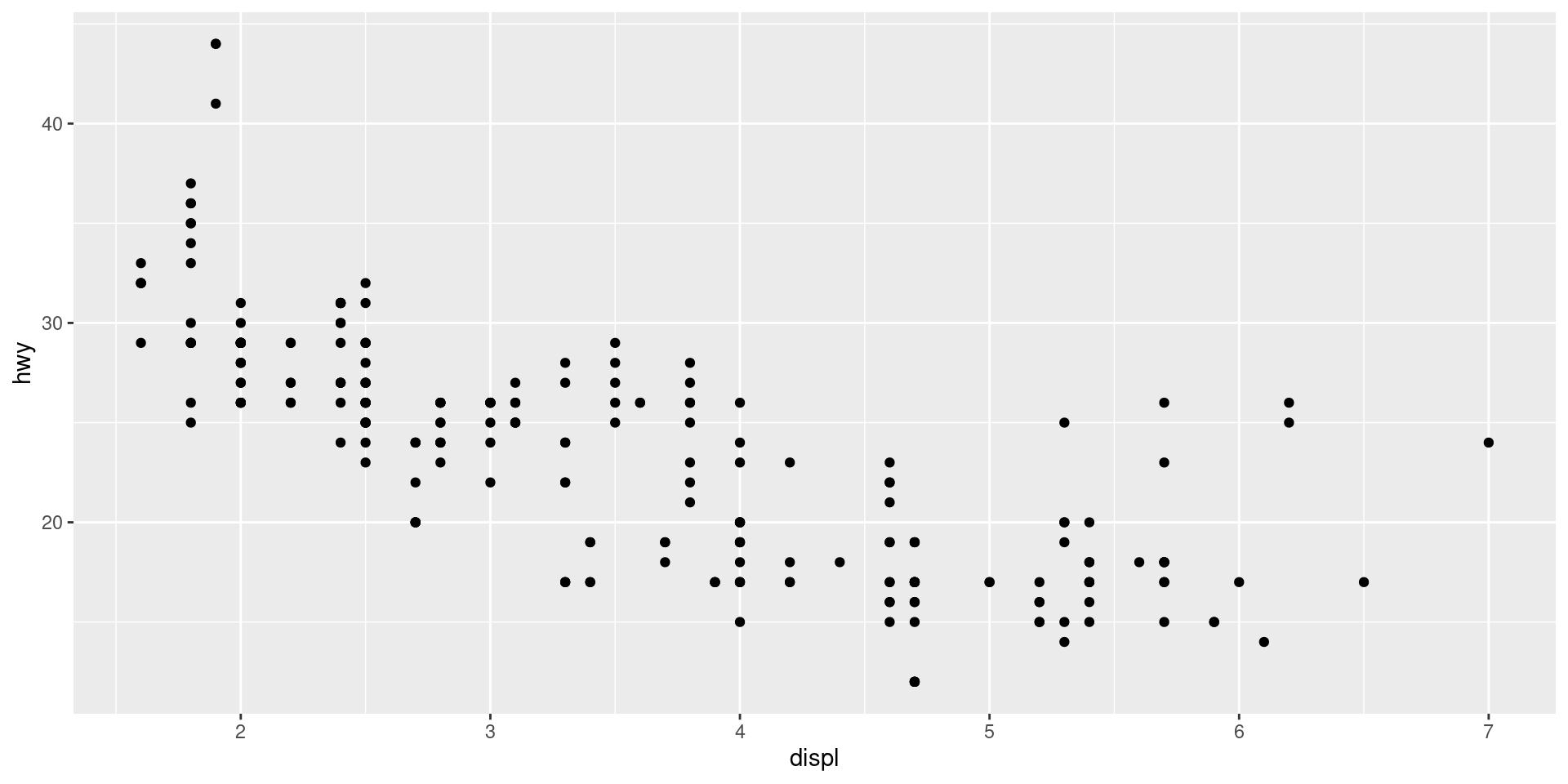
Plot points
How is this different? What are advantages/disadvantages?
mpg |>
ggplot() +
geom_point(aes(x = displ, y = hwy))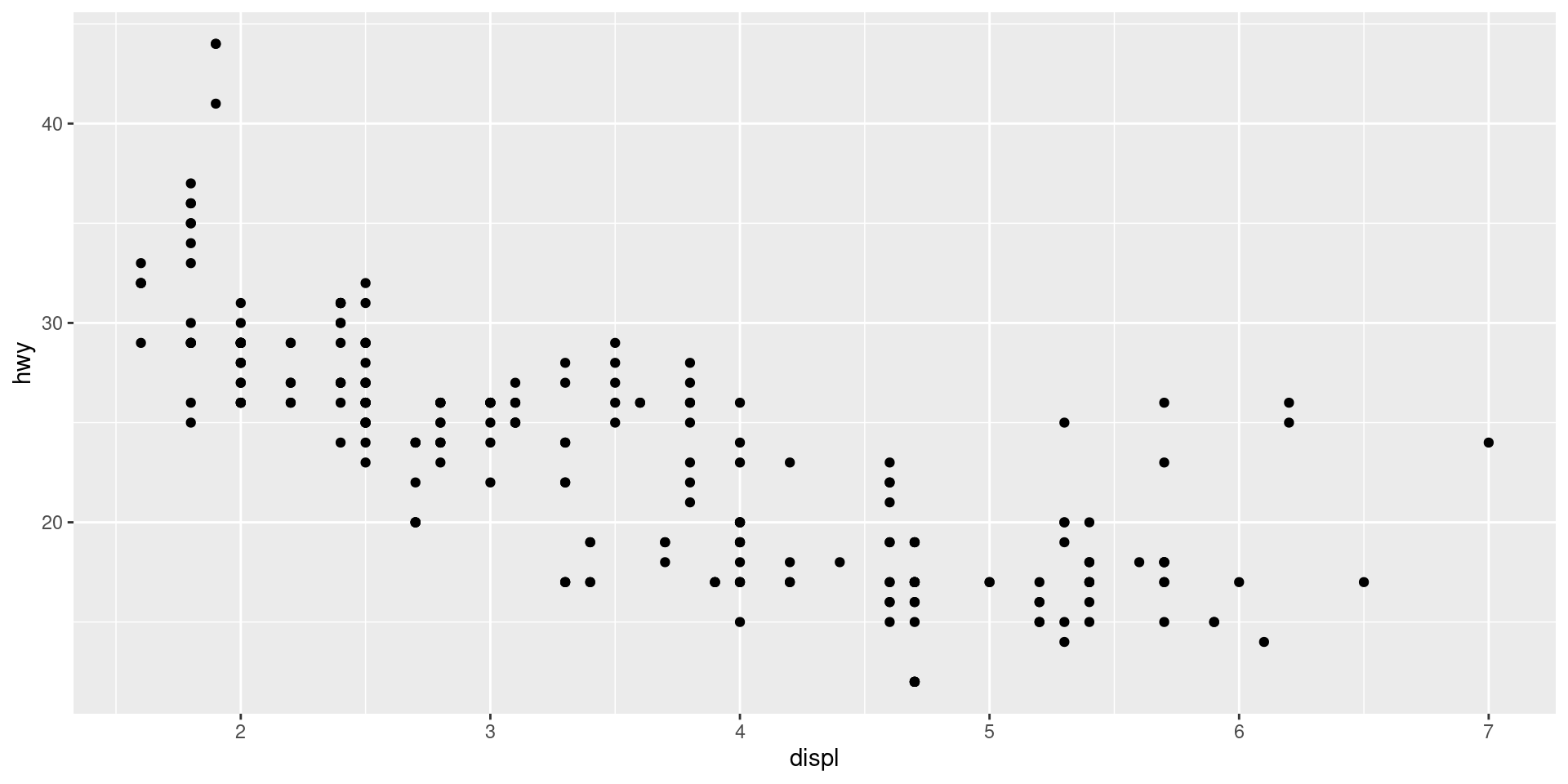
Plot smooth lines
#
mpg |>
ggplot(aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_smooth()
Plot multiple geoms
mpg |>
ggplot(aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth()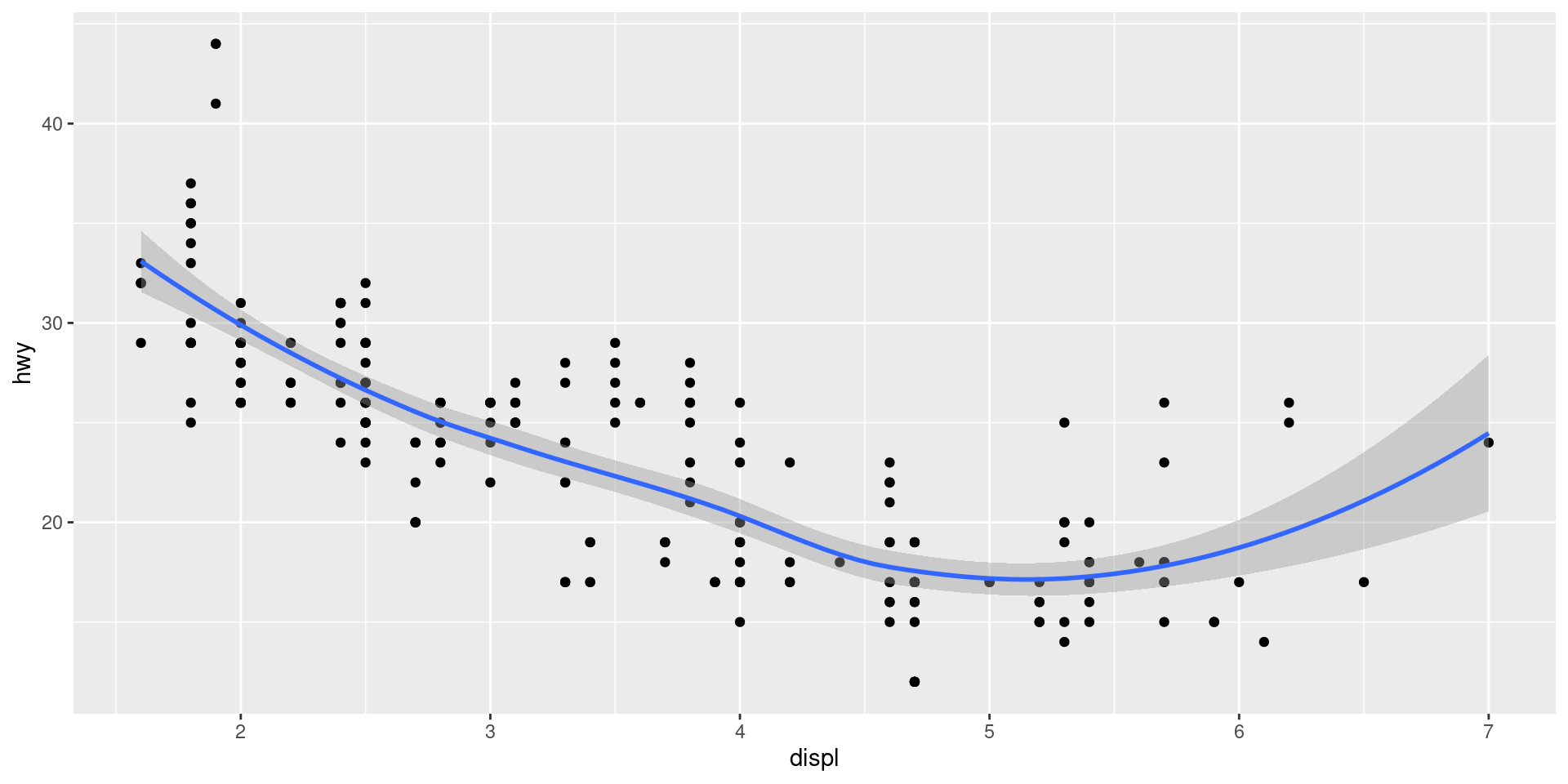
Order matters
mpg |>
ggplot(aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_smooth() +
geom_point()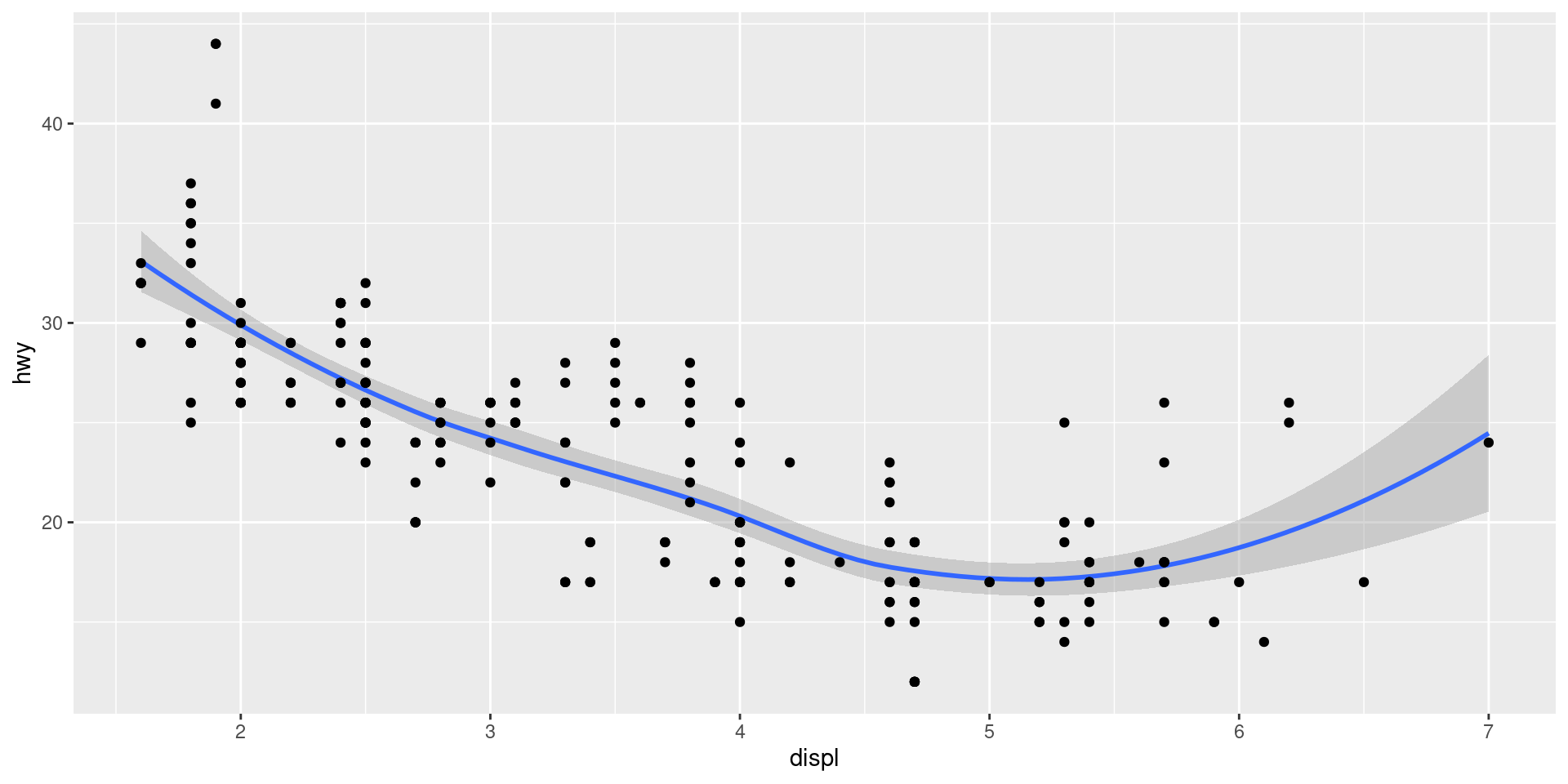
Plot linear regression line
mpg |>
ggplot(aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = "lm")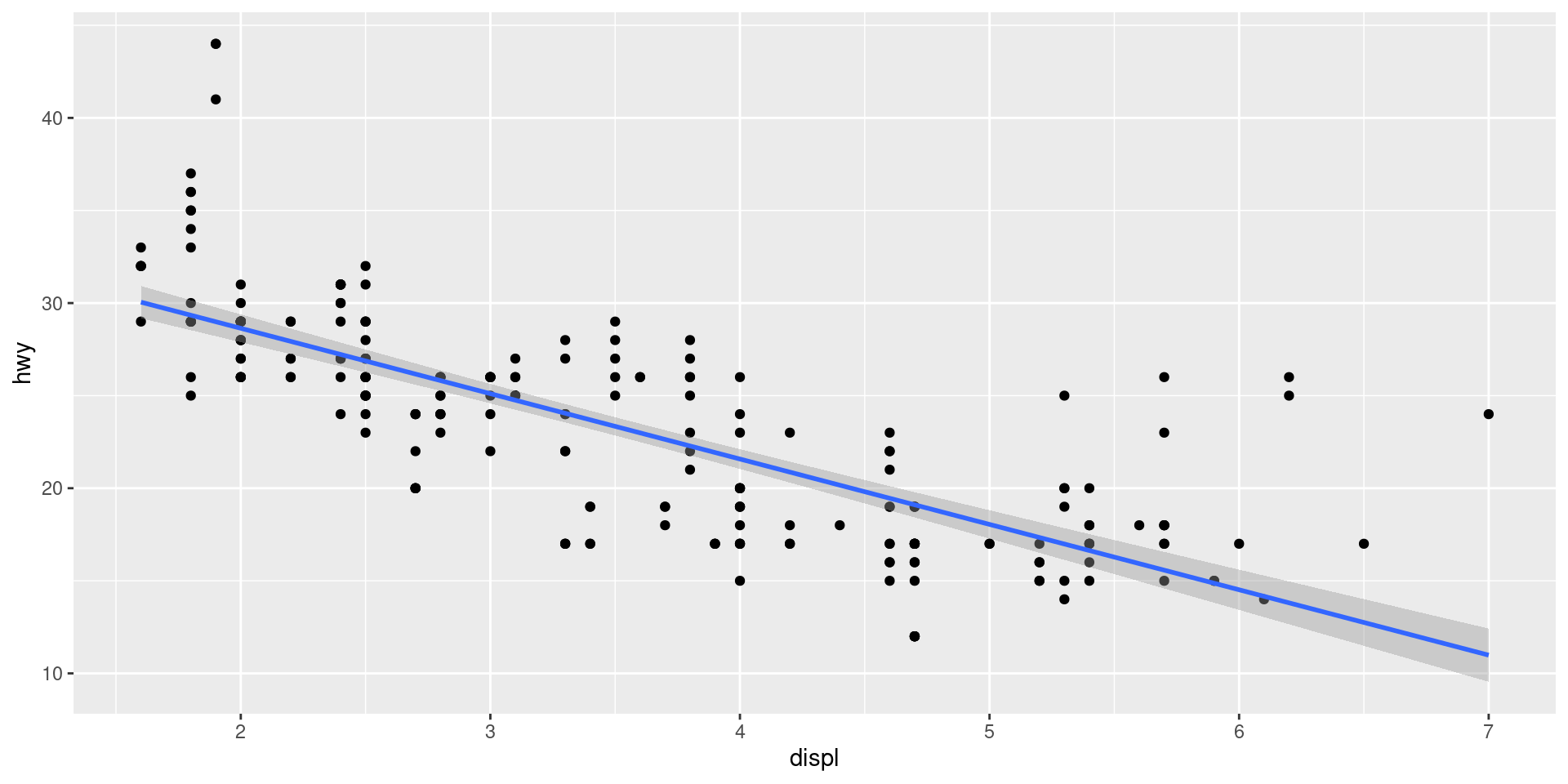
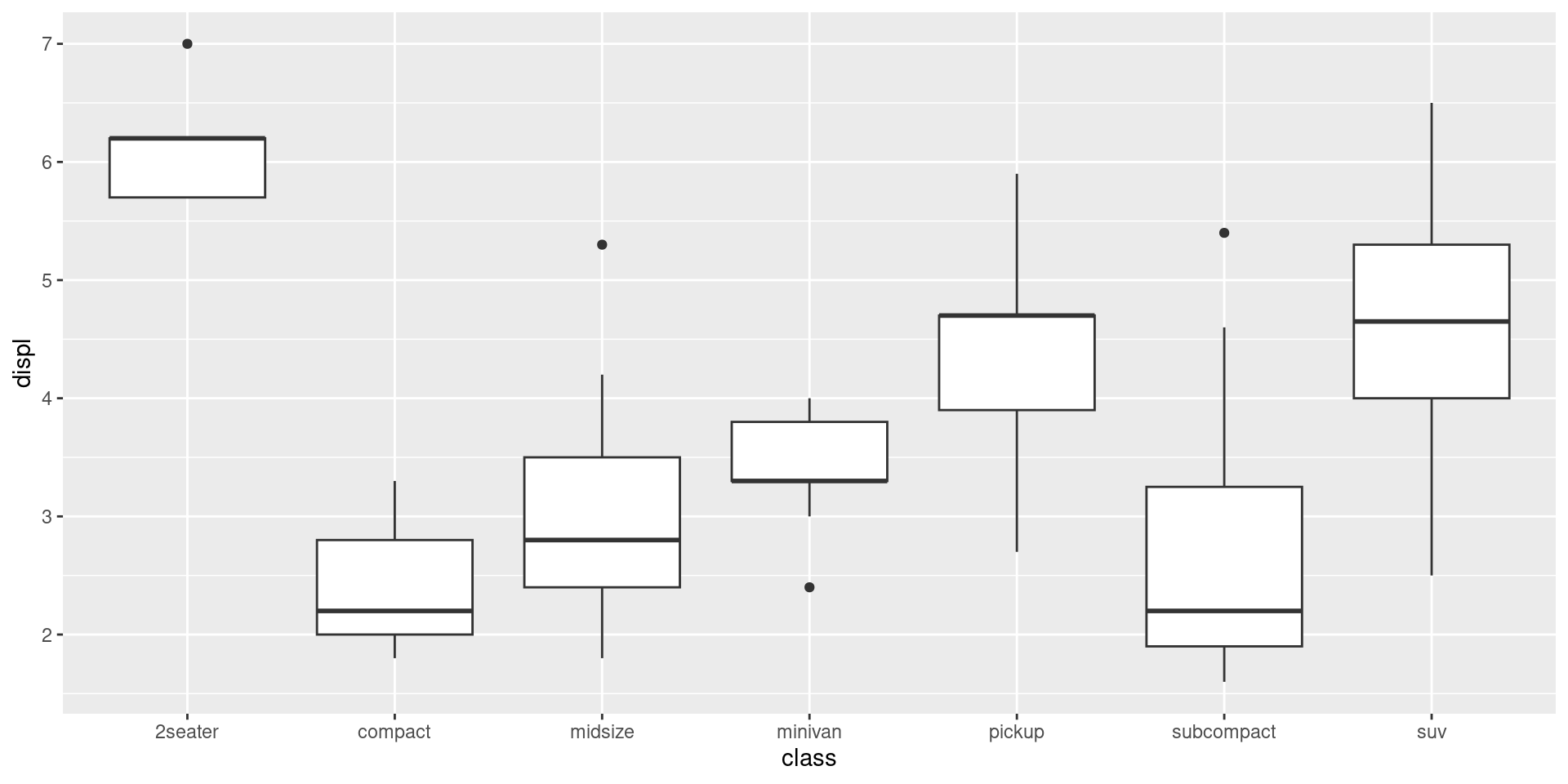
Plot boxplots
mpg |>
ggplot(aes(x = class, y = displ)) +
geom_boxplot()